How do I make an HTTP request in Javascript?
To make an HTTP request in JavaScript, you can use the XMLHttpRequest object or the fetch() function.
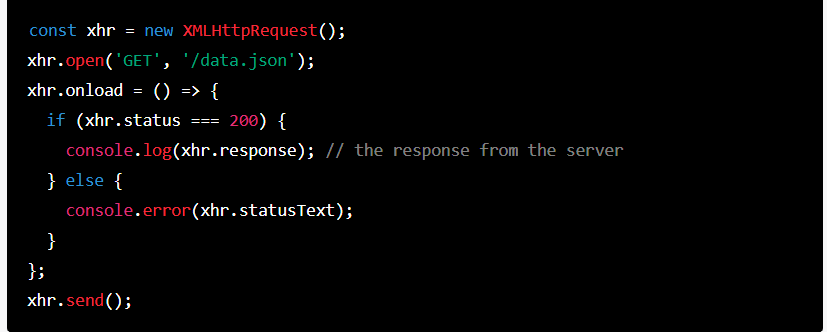
Here’s an example of using XMLHttpRequest to make an HTTP GET request to retrieve data from a JSON file:
| const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(); xhr.open(‘GET’, ‘/data.json’); xhr.onload = () => { if (xhr.status === 200) { console.log(xhr.response); // the response from the server } else { console.error(xhr.statusText); } }; xhr.send(); |
And here’s an example of using fetch() to make the same request:
| fetch(‘/data.json’) .then(response => { if (response.ok) { return response.json(); } else { throw new Error(‘Request failed’); } }) .then(data => { console.log(data); // the response from the server }) .catch(error => { console.error(error); }); |
Both of these examples make an HTTP GET request to retrieve data from a JSON file located at ‘/data.json’. The XMLHttpRequest example uses xhr.open() to specify the request method (‘GET’) and the URL of the resource to be fetched, and xhr.send() to send the request. The fetch() example uses the fetch() function to specify the URL of the resource to be fetched, and returns a promise that resolves to a Response object. The Response object has a json() method that returns a promise that resolves to the JSON-parsed response body.
You can also use XMLHttpRequest or fetch() to make other types of HTTP requests, such as POST, PUT, DELETE, etc. You can specify the request method and any request headers by using the appropriate methods of the XMLHttpRequest object or the options object passed to fetch().










